Preemptive non-selective bronchial artery angioembolization to reduce recurrence rate of hemoptysis
Keywords:
Bronchial artery, angioembolization, hemoptysis, recurrenceAbstract
Background: Massive hemoptysis which is presented in advanced lung diseases is a life-threatening condition. Bronchial artery embolization as a minimally invasive procedure is the treatment of choice either in first or recurrent hemoptysis. This study aimed to assess the early and late efficacy of bronchial angioembolization (BAE) without microcatheter.
Methods: In this prospective cohort study, all patients with hemoptysis who had undergone BAE from August 2018 to March 2019 were included. Angiographic patterns including bleeding sources, number of involved vessels, the underlying etiology, and recurrence rate were evaluated in a one-year follow-up.
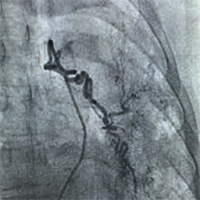
Results: 153 patients were included with mean age of 55 ±16 years. 68% of them were male and 58% had life-threatening massive hemoptysis. Three distinct angiographic patterns were recognized. The culprit bleeding vessel was bronchial in 126 (92%), intercostal in 4 (3%), and both vessels in 7 (5%) of cases (P<0.05). One vessel involvement was seen in 56 patients; however it was observed in 69% of non-cystic fibrosis lobar bronchiectasis patients. In 1, 3 and 12 months follow up, recurrent hemoptysis was reported in 15 (11%), 4 (2.5%), and 24 (15.5%), respectively. In 52% of cases, no abnormal vessels were observed during aorta injection, but culprit bronchial or intercostal arteries were found in selective investigational angiography.
Conclusion: BAE was successful in the control of hemoptysis and resulted in a low rate of recurrence in different types of lung diseases. This could be due to the embolization of all pathological arteries found during angiography which might have prevented recurrent bleeding.
References
Adachi T, Oki M, Saka H. Management considerations for the treatment of idiopathic massive hemoptysis with endobronchial occlusion combined with bronchial artery embolization. Intern Med 2016;55:173–7.
Albahhar M, Vo HA, Bowers H, Keshavamurthy J, Rotem E. Embolization of non-bronchial systemic artery (inferior phrenic) as a source of massive hemoptysis in a patient with mycobacterial bronchiectasis. Am Thorac Soc 2017;195:A1491.
Khanal N, Shi H-B. Outcomes of bronchial artery embolization in massive hemoptysis of various etiologies. Sci Lett 2017;5:138–45.
Yoon W, Kim JK, Kim YH, Chung TW, Kang HK. Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: a comprehensive review. Radiographics 2002;22:1395-409.
Jean-Baptiste E. Clinical assessment and management of massive hemoptysis. Crit Care Med 2001;29:1098.
Xie M. Value of radiodensity determined by enhanced computed tomography for the differential diagnosis of lung masses. Iran J Radiol 2011;8:145.
Gupta A, Sands M, Chauhan NR. Massive hemoptysis in pulmonary infections: bronchial artery embolization. J Thorac Dis 2018;10:S3458.
O’Dell MC, Gill AE, Hawkins CM. Bronchial artery embolization for the treatment of acute hemoptysis. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 2017;20:263–5.
Chun J-Y, Belli A-M. Immediate and long-term outcomes of bronchial and non-bronchial systemic artery embolisation for the management of haemoptysis. Eur Radiol 2010;20:558-65.
White RI. Bronchial artery embolotherapy for control of acute hemoptysis: analysis of outcome. Chest 1999;115:912-5.
Tanaka N, Yamakado K, Murashima S, Takeda K, Matsumura K, Nakagawa T, et al. Superselective bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis with a coaxial microcatheter system. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1997;8:65-70.
Do K-H, Goo JM, Im J-G, Kim KW, Chung JW, Park JH. Systemic arterial supply to the lungs in adults: spiral CT findings. Radiographics 2001;21:387-402.
Mal H, Rullon I, Mellot F, Brugiere O, Sleiman C, Menu Y, et al. Immediate and long-term results of bronchial artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest 1999;115:996-1001.
Goh PY-T, Lin M, Teo N, Wong DES. Embolization for hemoptysis: a six-year review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2002;25:17-25.
Shigemura N, Wan IY, Simon CH, Wong RH, Hsin MKY, Thung HK, et al. Multidisciplinary management of life-threatening massive hemoptysis: a 10-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:849–53.
Knott-Craig CJ, Oostuizen JG, Rossouw G, Joubert JR, Barnard PM. Management and prognosis of massive hemoptysis Recent experience with 120 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1993;105:394–7.
Valipour A, Kreuzer A, Koller H, Koessler W, Burghuber OC. Bronchoscopy-guided topical hemostatic tamponade therapy for the management of life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest 2005;127:2113–8.
Fartoukh M, Khalil A, Louis L, Carette M-F, Bazelly B, Cadranel J, et al. An integrated approach to diagnosis and management of severe haemoptysis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit: a case series from a referral centre. Respir Res 2007;8:11.
Sedghi GN, Adimi NP, Miri M, Malek MM, Pejhan S. Massive hemoptysis: diagnostic approach, risk factors and outcome in six years experience. NAFAS J 2015;2:41-7.
Davidson K, Shojaee S. Managing massive hemoptysis. Chest 2020;157:77–88.
Tsoumakidou M, Chrysofakis G, Tsiligianni I, Maltezakis G, Siafakas NM, Tzanakis N. A prospective analysis of 184 hemoptysis cases–diagnostic impact of chest X-ray, computed tomography, bronchoscopy. Respiration 2006;73:808–14.
Mondoni M, Carlucci P, Job S, Parazzini EM, Cipolla G, Pagani M, et al. Observational, multicentre study on the epidemiology of haemoptysis. Eur Respir J 2018;51:1701813.
Hsiao EI, Kirsch CM, Kagawa FT, Wehner JH, Jensen WA, Baxter RB. Utility of fiberoptic bronchoscopy before bronchial artery embolization for massive hemoptysis. Am J Roentgenol 2001;177:861–7.
Abal AT, Nair PC, Cherian J. Haemoptysis: aetiology, evaluation and outcome—a prospective study in a third-world country. Respir Med 2001;95:548–52.
Fruchter O, Schneer S, Rusanov V, Belenky A, Kramer MR. Bronchial artery embolization for massive hemoptysis: long-term follow-up. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 2015;23:55–60.
Seyyedi SR, Sadeghipour P, Sadr M, Shafe O, Moosavi J, Aloosh O, et al. Outcomes and complications of bronchial angioembolization in patients with massive hemoptysis. Tanaffos 2019;18:310–4.
Jougon J, Ballester M, Delcambre F, Mac Bride T, Valat P, Gomez F, et al. Massive hemoptysis: what place for medical and surgical treatment. Eur J Cardio-Thoracic Surg 2002;22:345–51.
Springer D, Cofta S, Juszkat R, Żabicki B, Goździk-Spychalska J, Nowicka A, et al. The effectiveness of bronchial artery embolisation in patients with haemoptysis. Adv Respir Med 2018;86:220–6.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Mattioli 1885 has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.




